Randomized Controlled Trial (RCT) of...
Smart Beginnings, A Birth to Age 3 Parenting Program for Low-Income Families
Reviewed
Pediatrics (January 2026) published RCT findings for Smart Beginnings, a birth to age 3 parenting program for low-income families. Despite the study abstract’s positive portrayal of the findings on child academic outcomes at age 6, the RCT results were null for all five academic outcomes reported in the paper – measuring language, literacy, and math skills.
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: Despite longstanding efforts to design, implement, and study parenting interventions early in life to address disparities in school readiness, gaps remain related to understanding their long-term effects and pathways of influence on child development. Here we describe sustained impacts at child age 6 of the innovative, tiered birth to age 3 Smart Beginnings (SB) model.
METHODS: We performed a single-blind, 2-site randomized clinical trial of the SB model. SB integrates PlayReadVIP, a universal, pediatric primary care–based program, and Family Check-Up, a targeted secondary home-based parenting intervention. Mother-infant dyads (N = 403) were randomized at birth to standard pediatric care or the SB model. In line with SB’s theory of change that supporting parents will promote their children’s development, single and serial mediation pathways evaluated intervention effects of SB on age 6 child academic skills through parental cognitive stimulation at age 2 and child academic functioning at age 4.
CONCLUSIONS: Findings build on the demonstrated scalability of the SB model, support the cumulative process of academic functioning in childhood, and offer a promising model to address disparities early in life.
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: Despite longstanding efforts to design, implement, and study parenting interventions early in life to address disparities in school readiness, gaps remain related to understanding their long-term effects and pathways of influence on child development. Here we describe sustained impacts at child age 6 of the innovative, tiered birth to age 3 Smart Beginnings (SB) model.
METHODS: We performed a single-blind, 2-site randomized clinical trial of the SB model. SB integrates PlayReadVIP, a universal, pediatric primary care–based program, and Family Check-Up, a targeted secondary home-based parenting intervention. Mother-infant dyads (N = 403) were randomized at birth to standard pediatric care or the SB model. In line with SB’s theory of change that supporting parents will promote their children’s development, single and serial mediation pathways evaluated intervention effects of SB on age 6 child academic skills through parental cognitive stimulation at age 2 and child academic functioning at age 4.
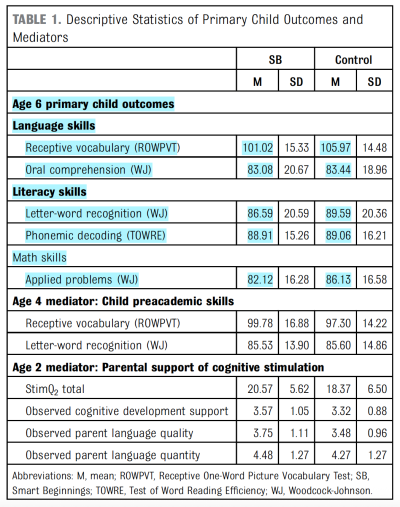
RESULTS: We found no statistically significant differences in child academic outcomes at age 6 between the SB group and the control group. In exploratory analyses of causal pathways, we found significant single and serially mediated indirect effects of SB on academic outcomes through parental cognitive stimulation in toddlerhood and preacademic skills in preschool. The total indirect pathways were positive and statistically significant for all academic outcomes at age 6, including receptive vocabulary (effect size [ES] = 0.04, P = .04), oral comprehension (ES = 0.05, P = .04), letter-word recognition (ES = 0.04, P = .04), phonemic decoding (ES = 0.04, P = .04), and applied problems (ES = 0.05, P = .04).
CONCLUSIONS: Findings build on the demonstrated scalability of the SB model,
but do not support the model’s hypothesized effects on child academic outcomes at age 6. Exploratory findings
support the cumulative process of academic functioning in childhood, and
provide insights for future research
offer a promising model to address disparities early in life.
No-Spin’s Study Overview
High-quality RCT of Smart Beginnings – a birth to age 3 parenting program for low-income families – finds no discernible impacts on child language, literacy, or math skills at age 6.
Program:
- Per the study report: “Smart Beginnings (SB) is an innovative, tiered birth to age 3 years parenting model designed to prevent poverty-related disparities in child development and school readiness. It integrates a universal health care–based intervention, PlayReadVIP, with a targeted home-based intervention, the Family Check-Up (FCU).”
Study Design:
- The study randomly assigned 403 Medicaid-eligible mothers in Pittsburgh and New York City who had recently given birth to a healthy infant to Smart Beginnings (treatment) versus usual primary care (control).
- Based on our careful review, this was a high-quality RCT (e.g. baseline balance, modest sample attrition, successful program implementation, preregistered outcomes).
Findings:
- The study found no discernible effects on any of the age-6 child academic outcomes reported on in the paper, including receptive vocabulary, oral comprehension, letter-word recognition, phonemic decoding, and math applied problems.
- As shown in the following table, the pattern of effects on these outcomes slightly favored the control group, although none were statistically significant.
Click or tap a highlight to see No-Spin’s comment